Qualcomm's latest acquisition of an AI startup isn't just another corporate purchase. It's a clear signal that the company is repositioning itself deeper into the Internet of Things market with a tighter focus on intelligent edge computing. The startup, whose name remains confidential pending regulatory approval, is recognized for its lightweight AI models, which are optimized for low-power devices, making it a strong fit for Qualcomm's chipset ecosystem.
Rather than investing in massive cloud-based models, this deal shows Qualcomm doubling down on AI inference that happens directly on-device, where milliseconds and battery life matter most. This isn't about chasing headlines—it's about control, performance, and staying ahead in the next generation of connected devices.
At the heart of this acquisition is a common problem in the IoT world: balancing intelligence with efficiency. Devices such as home assistants, industrial sensors, security cameras, and wearables all require local data processing without draining power or relying too heavily on cloud infrastructure. The startup that Qualcomm brought in has been working quietly on neural network compression and quantization techniques that enable large AI models to run on small devices without significant performance tradeoffs. That's exactly what Qualcomm wants to scale.
By folding this technology into its Snapdragon platform and related IoT chipsets, Qualcomm aims to offer ready-to-deploy AI solutions for device manufacturers. Rather than building from scratch or relying on cloud integrations, brands using Qualcomm chips will get access to edge-ready AI that’s already optimized for real-time processing. This could mean faster object recognition in cameras, smarter automation in factories, or voice assistants that don’t need to ping a server every time you speak.
It also addresses Qualcomm's interest in minimizing reliance on third-party AI infrastructure. As privacy issues increase and latency turns into a bottleneck, there is pressure throughout the industry to enable devices to "think" independently. Qualcomm's ownership of both the silicon and the AI layers may become a major differentiator in this area. While other firms attempt to attach AI capabilities to general-purpose processors, Qualcomm seeks its chips to be born with it.
The timing of this deal isn't random. AI in IoT is shifting from proof of concept to wide deployment, and hardware makers are racing to provide the right foundation. Qualcomm's main competitors, such as NVIDIA in the industrial edge space and Apple in the mobile arena, are already customizing their own AI pipelines. Apple has its Neural Engine embedded in every iPhone. NVIDIA is pushing Jetson for robotics and smart infrastructure. Qualcomm doesn't want to be just another hardware provider; it wants to be part of the intelligence stack.

With this startup's expertise now on board, Qualcomm can fine-tune its AI toolkits for developers. That includes more efficient model training, better on-device inference engines, and pre-trained models that work across product lines. Developers using Qualcomm chips can expect improvements in AI runtime, especially in areas like gesture recognition, predictive maintenance, and local anomaly detection. These features are essential for making IoT devices truly useful, rather than just connected.
What’s interesting is that the startup isn’t just bringing tech—it’s bringing talent. The engineering team reportedly includes veterans from Google Brain and smaller research labs focused on embedded AI. That kind of skillset is hard to build internally and even harder to buy. Qualcomm is not only acquiring code, but a pipeline of ideas that could reshape how its future hardware evolves.
This matters for another reason: regulation and trust. With increased scrutiny around where and how AI models are trained, having in-house AI control means Qualcomm won't have to rely on opaque cloud-based APIs or partnerships with firms facing data concerns. Everything, from the model to the chip, can be handled in-house, allowing Qualcomm to offer end-to-end secure AI systems for critical industries such as healthcare, automotive, and smart cities.
Qualcomm’s IoT strategy has leaned on hardware reliability and power management. With this acquisition, the message shifts—performance now includes intelligence. As developers and OEMs seek AI at the edge, Qualcomm’s integrated approach can save time, complexity, and compliance issues.
This also repositions Qualcomm for software developers. Historically focused on chip specs and benchmarks, Qualcomm now emphasizes developer ecosystems. Think plug-and-play AI for cameras, speakers, thermostats, or drones—where Qualcomm’s tools become the backbone.
Qualcomm recognizes AI isn’t just about size or speed—it’s about where and how it runs. Cloud AI is powerful but often impractical. Privacy laws, bandwidth limits, and latency make on-site intelligence necessary for many IoT uses. By acquiring a startup focused on edge AI, Qualcomm shows its belief that smarter chips beat bigger clouds.
The economics matter too. By building AI into chipsets, Qualcomm adds value without increasing footprint or energy cost. That appeals to partners in automotive, smart appliances, and industrial automation, where margins are tight and deployment must scale. It also differentiates Qualcomm from its rivals, which are slower to integrate AI into silicon.
The Qualcomm AI acquisition isn’t just buying a company—it’s buying a future. As edge computing becomes central to devices, AI that is lightweight and capable is no longer a bonus—it’s expected. Qualcomm is building an ecosystem where its chips do more than process—they anticipate, detect, and respond.

This shift will likely appear in the company’s roadmap over the next year. Expect new chipsets supporting the startup’s models, developer kits for edge AI, and case studies showing gains in performance or battery life. Qualcomm might even open-source parts of the stack to build trust with developers.
There’s still a long road. Qualcomm must integrate the startup’s tech without adding friction. If it succeeds, the company could strengthen its lead in AI-driven IoT. While others talk about “smart” devices, Qualcomm’s chips might deliver that—not in theory, but in code.
Qualcomm’s acquisition signals a shift from chipmaker to full-stack AI provider for IoT. By integrating edge-ready AI, it brings smarter, faster, more autonomous intelligence to connected devices. This practical move reduces cloud dependency while improving responsiveness and user experience. The change may feel invisible to users, yet their devices will anticipate needs and act more intelligently. Rather than adding superficial features, this approach reshapes what smart technology delivers, making everyday interactions with connected devices more seamless and genuinely helpful.
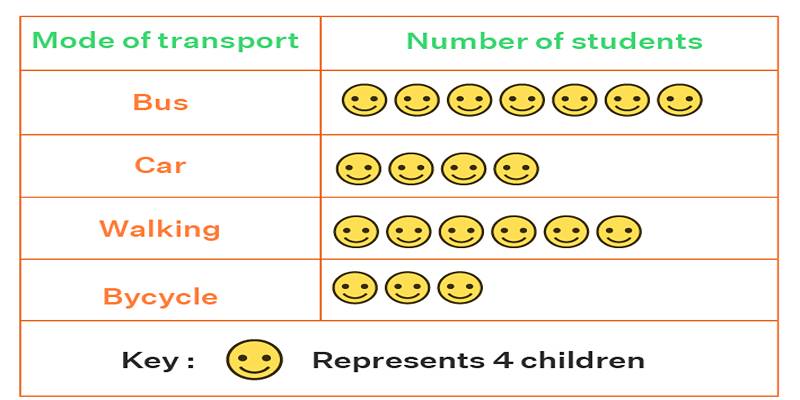

Learn what a pictogram graph is, how it's used, and why it's great for data visualization. Explore tips, examples, and benefits.

Knowledge representation in AI helps machines reason and act intelligently by organizing information in structured formats. Understand how it works in real-world systems

How the AI Hotel Planned for Las Vegas at CES 2025 is set to transform travel. Explore how artificial intelligence in hospitality creates seamless, personalized stays for modern visitors

Explore the role of probability in AI and how it enables intelligent decision-making in uncertain environments. Learn how probabilistic models drive core AI functions

How the FILM model uses a scale-agnostic neural network to create high-quality slow-motion videos from ordinary footage. Learn how it works, its benefits, and its real-world applications

Boost your Amazon sales by optimizing your Amazon product images using ChatGPT. Learn how to craft image strategies that convert with clarity and purpose
How to visualize proteins using interactive, AI-powered tools on Hugging Face Spaces. Learn how protein structure prediction and web-based visualization make research and education more accessible

How AWS Braket makes quantum computing accessible through the cloud. This detailed guide explains how the platform works, its benefits, and how it helps users experiment with real quantum hardware and simulators

AI in Agriculture is revolutionizing farming with advanced crop monitoring and yield prediction tools, helping farmers improve productivity and sustainability

Uncover how The Turing Test shaped our understanding of artificial intelligence and why modern AI evaluation methods now demand deeper, task-driven insights

The development of chatbots throughout 2025 will lead to emerging cybersecurity threats that they must confront.

Nvidia Acquires Israeli AI Startup for $700M to expand its AI capabil-ities and integrate advanced optimization software into its platforms. Learn how this move impacts Nvidia’s strategy and the Israeli tech ecosystem