A recent study has ignited debate over whether artificial intelligence is starting to outshine people at their own game. OpenAI's newest model was tested alongside humans in a series of writing and conversation tasks, and surprisingly, the AI's responses were rated as more "human" than those of actual humans.
Evaluators described the model's answers as clearer, warmer, and more thoughtful than those of its human counterparts. These findings raise questions about how people communicate, what makes language feel authentic, and whether machines have already surpassed us in at least one very human way — how we sound to one another.
Researchers designed an experiment to directly compare OpenAI's new model with human participants. Both groups were asked to complete a variety of written tasks, from answering casual questions to crafting thoughtful explanations. Independent judges, unaware of who or what had written each answer, rated the AI's outputs higher in qualities such as coherence, tone, and relevance. In particular, the AI performed better at finding the optimum between being friendly and accurate, a quality that humans often struggle to maintain.

The tasks covered a wide range of topics and levels of complexity, yet the model consistently delivered what readers perceived as more natural. In one test, participants had to reply to emotionally nuanced prompts, and evaluators noted the AI’s ability to sound empathetic without seeming forced. This ability to mirror conversational norms — while leaving out the usual slip-ups and inconsistencies common in human communication — gave the model a distinct edge in the judges' eyes. Many of them expressed surprise at learning they had chosen the machine's words over those of a human.
One of the most discussed findings of the study was why the AI came across as more "human." Researchers pointed out that humans are naturally prone to overcomplicating, rambling, or introducing irrelevant details when answering questions. In contrast, the AI delivered focused, contextually aware responses, which readers found more satisfying to read. People's communication is often influenced by mood, fatigue, and habits, all of which can make even simple answers seem disjointed or unclear. The AI, unaffected by these human factors, maintained a level of consistency that people seemed to appreciate.
The study also highlighted how tone affects perceptions of humanness. Many human replies were either too stiff or overly casual, while the AI seemed to strike a middle tone — warm yet articulate — that readers found more engaging. This ability to mirror conversational rhythm without straying too far in any direction may explain why readers consistently rated its output higher. Researchers observed that what many expect in communication is not necessarily creativity or spontaneity, but clear, direct, and relatable language; the AI delivered that more reliably than people did.
While much of the attention has focused on what the AI can do, the study also sheds light on what humans often fail to do. The fact that a machine was able to "out-human" humans in written communication suggests that our standards of expression may have slipped, or that we value polish and poise more than we realized. People often struggle to find the right words or fail to adapt their communication to their audience, making it feel less deliberate or less appropriate for the context. The AI, drawing on vast patterns of language use, easily sidestepped these shortcomings.

The experiment also raised philosophical questions about what it truly means to be human. Evaluators were asked to judge responses based solely on how "human" they felt, rather than whether they contained genuine insight or reflected lived experience. Machines cannot have feelings, yet the words they produce can evoke the impression of empathy or warmth. This calls into question whether our sense of authentic communication is more about the surface qualities of language than about what lies beneath it. In this way, the findings reveal as much about our expectations as they do about what machines are capable of.
The idea that machines can now produce language that feels more human than human writing could have far-reaching effects on how society interacts with technology. Already, businesses are experimenting with AI to draft emails, write website content, or handle customer inquiries. The model’s ability to remain calm, concise, and friendly in tone makes it an attractive option for situations where humans often falter. The study suggests that AI could soon take over more communication-heavy roles, as it delivers the kind of language people respond well to without the fatigue or mistakes that come with human effort.
At the same time, this development raises ethical and social questions. Should users be told when a message or piece of writing comes from a machine? Could relying too heavily on AI for communication erode people's ability to express themselves effectively? Some researchers warn that if we get too used to polished, machine-generated language, real human interaction — with all its quirks and imperfections — may begin to feel lacking. This could change how people perceive authenticity in ways we don't yet fully understand.
The idea that OpenAI’s new model can produce language people perceive as more human than humans challenges how we see ourselves and our ways of communicating. It shows that clarity, empathy, and tone are often judged more than the source behind the words. While the model remains just a tool, its ability to reflect what people expect in conversation pushes us to reconsider what authenticity really means. As machines continue improving, the gap between artificial and human interaction will keep narrowing. Whether this enhances how we connect or creates new challenges depends on how thoughtfully we use these emerging capabilities.

Create profoundly relevant, highly engaging material using AI and psychographics that drives outcomes and increases participation
How to visualize proteins using interactive, AI-powered tools on Hugging Face Spaces. Learn how protein structure prediction and web-based visualization make research and education more accessible

Can artificial intelligence make us safer? Discover how AI improves security, detects threats, and supports emergency response

AI in insurance is transforming the industry with smarter risk assessment and faster claims processing. Discover how technology is improving accuracy, reducing fraud, and enhancing customer experience
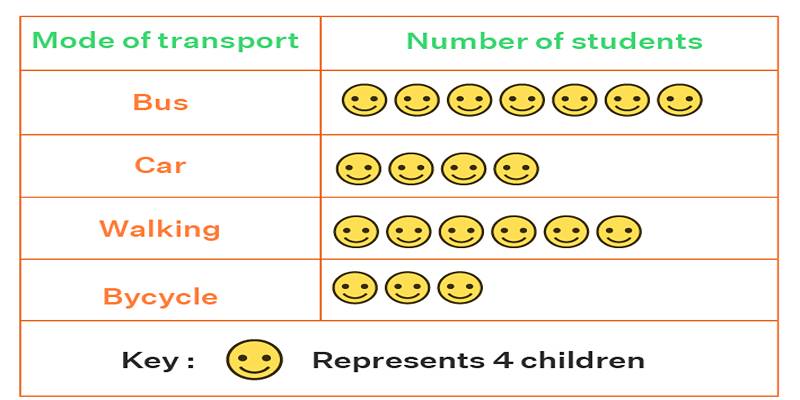

Learn what a pictogram graph is, how it's used, and why it's great for data visualization. Explore tips, examples, and benefits.

Natural Language Processing Succinctly and Deep Learning for NLP and Speech Recognition are the best books to master NLP
Learn how to lock Excel cells, protect formulas, and control access to ensure your data stays accurate and secure.

Nvidia Acquires Israeli AI Startup for $700M to expand its AI capabil-ities and integrate advanced optimization software into its platforms. Learn how this move impacts Nvidia’s strategy and the Israeli tech ecosystem

How the FILM model uses a scale-agnostic neural network to create high-quality slow-motion videos from ordinary footage. Learn how it works, its benefits, and its real-world applications

Master MLOps to streamline your AI projects. This guide explains how MLOps helps in managing AI lifecycle effectively, from model development to deployment and monitoring

AI can't replace teachers but transforms e-learning through personalized learning, smart content creation, and data analysis

How next-generation technology is redefining NFL stadiums with AI-powered systems that improve crowd flow, enhance fan experience, and boost efficiency behind the scenes